Emergency Change Management | Emergency Change Management Process
What is Emergency Change ?
A Change is nothing but shifting/transitioning/modifying/from its current state to a desired future state. Any change implemented to restore service or avoid an outage of service significantly impacts multiple users. Emergency changes would need Emergency CAB approvals to validate and approve the change.
Emergency Change Management
Objectives
The objective of Emergency Change Management is to:
- To define a standard procedure for handling emergency changes in the infrastructure.
- To understand the urgency of emergency changes and implement them without creating any incidents.
- To ensure changes are successfully deployed, at the first attempt.
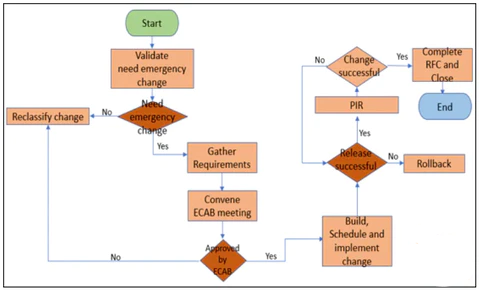
Emergency Change Management Process flow
In a practical IT environment, change management operations would generally be executed as per the below diagram:
Change Management Flow - Process Description of Emergency Change Management
Change Trigger/Input
Emergency change is triggered when a major incident occurs or when an important issue is about to happen (like a security upgrade, regulatory requirement, etc.)
Every emergency change ticket should be recorded to be tracked, monitored, and updated throughout its life cycle; no emergency changes can be implemented based on verbal/ email communications.
Emergency Change Validation
When a Major Incident happens, an Emergency Change may have to be deployed into Production (The trigger for Emergency Change Management is constantly via the Major Incident). The Emergency Change management process gets triggered by logging an Emergency Change in Remedy with appropriate categorization.
The change Manager will be notified of the Emergency Change.
The change Manager will validate the need for an Emergency Change in consultation with Major Incident Manager, who will be the Change Owner in this case.
Need emergency change
Change Manager, in consultation with Change Owner, will ascertain whether the change is an Emergency Change.
Gather Requirements
If an Emergency Change is triggered, Change Owner will be ready with all functional & technical requirements and then document the impact of Change if implemented and back out readiness.
Convene ECAB meeting
Change Manager convenes the I-CAB so that the emergency change can be discussed for approval. E-CAB is assembled based on the urgency of the situation. This meeting may be conducted via a bridge line opened by the Change Manager. Also, I-CAB members will be made aware of the urgency of the meeting.
Change Manager works in close cooperation with the Major Incident Manager towards implementing the solutions for major incidents via changes. Following (but not limited to) are the members of the E-CAB.
- Change Manager
- <<Customer>> Service Manager
- <<Customer>> <<Role>>
- Major Incident Manager
- Service Delivery Managers

ECAB Approval
E-CAB will consider the Change from an impact/cost perspective and either approve or not give their approval. The back-out plan has to be there and would be a mandatory requirement for supporting the change.
While a verbal approval may trigger the change to be built, it is mandatory to attach an approval email to the RFC. Without a documented permission, an Emergency Change should not be implemented.
Build, Schedule, and Implement Change
In case the Change is approved by the E-CAB, the Change is scheduled for implementation.
All relevant Technology Leads/ Experts are informed via broadcast mail by the Change Manager.
Relevant Resolver Group(s) would build, test, and implement the change. Testing would be performed based on the availability of a Test Environment. Testing is not detailed like that performed during a regular or expedited change in case of Emergency Changes.
Change Owner coordinates the change with the Release Manager. Minimal testing is carried out to gain confidence and also to avoid post-implementation issues.
Release successfully?
Once the Release is deployed (Change implemented), Resolver Group checks if the implementation is successful or not.
Change Manager will work with the Major Incident Manager and ensure that the service is restored at the earliest.
Rollback
In case the change is not successful, it would be rolled back by the Change Owner.
Complete RFC & Close
Once the Service is restored, RFC is updated by the Change Owner with the entire information in all aspects.
In the case of a failed change, RFC is updated with the relevant details.
PIR
The Change Manager triggers a Post Implementation Review meeting with the Change owner and other key stakeholders, CAB, on <<Day>> to check the impact of Changes on the environment and understand whether the Change met its goal or not.
Change successfully?
Once the Change is implemented, the Change Manager checks if the implementation is successful or not.
Change Manager will work with the Major Incident Manager and ensure that the service is restored at the earliest.
Reclassify change
Change is reclassified as normal/ standard change. Change Manager would seek business approval to classify the change as a regular/routine change.








